Financial Reports- Preparation of Balance Sheet
A balance sheet gives on the overview of one’s financial position of the company, sole proprietorship, private limited corporate or other government organizations. It helps in defining the position of assets, liabilities and equity of an organization at the end of financial year. Basically a balance sheet is prepared at the end of set period of time be it quarterly, annually or monthly. With the help of profit and loss statement, cash flow statements, balance sheet aids business owners to evaluate company’s financial standing.
It is a tool to monitor assets, liabilities and net worth of the company. Preparing and learning to draft a balance sheet is a skill which will help not only business owners but also investors, lenders and other stakeholders to Asses Company’s financial health. A Standard company balance sheet consists of two sides- Assets on the left side whereas Liabilities on the right side further categorized into two parts (long term, short term liabilities and ownership equity).
Balance sheet consists of following elements:
• Assets– Assets bring value and benefit to firms operations by generating cash flow, deducting expenses, improving sales etc. It reflects how assets being a valuable possession gets financed either by debt or equity in turn helps in generation of revenue and sufficient amount of profits.
It can be subdivided into two parts:
Current Assets– Current assets are those assets which becomes exhausted or consumed or sold while carrying out the normal operations of the company within its operating cycle or current financial year. In simple words those assets which can be readily converted into cash or liquid form within a fiscal year. It indicates the liquidity position of the company, how a company can readily convert its assets into cash. Investors, creditors and other shareholders analyses company’s current assets to have a clear view of risk or benefits involved in the operations.
List of current assets include:
i. Cash and cash equivalents – These are the most liquid assets with short term commitments that can be readily converted in terms of cash.
ii. Inventory- It refers to kept aside raw material, component and finished products for future use or in case of emergency.
iii. Pre-paid expenses – It refers to the payments made in advance by the company for those goods and services which will be received in the future. These are the assets which cannot be converted into cash but they free up the capital for other relevant uses.
iv. Accounts receivables- These are the payments which are held back for goods supplied and services rendered that were already ordered by the customers but not yet paid for it.
v. Marketable securities- These financial tools are highly liquid that are issued either for equity securities or debt securities. These can be easily sold due to its short-term maturities.
vi. Short- term investments-
Formulae of Current assets = Cash and cash equivalents + Inventory + Pre-paid expenses + Accounts receivables + Marketable securities + Short- term investments
Non- current assets– These are long term investments whose value cannot be completely realized within an accounting year. These assets cannot be monetized and thus helps business owners and investors to determine proficiency of the firm to use resources and come up with profitable avenue. These assets are purchased with a motive to use them for day-to-day operations for longer term.
List of non-current assets include:
i. Tangible assets- includes: Plant & Machinery, Furniture, Land & Building, Vehicles, Property and equipment.
ii. Non-tangible assets- includes: Goodwill, Patents, Trademark, etc.
iii. Non marketable investment
iv. Deferred income tax
v. Financial assets
vi. Long term investment
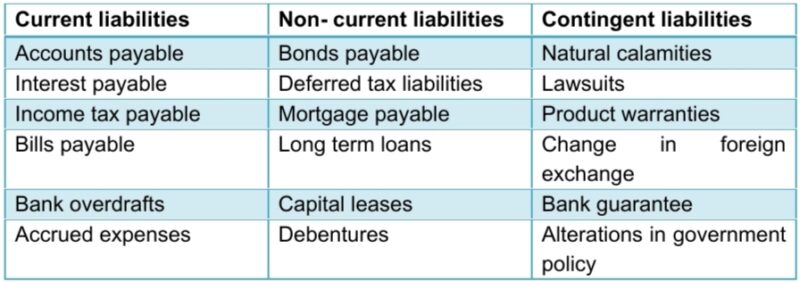
• Liabilities – Liability is referred to as an amount which an individual or a company owes. As a result to the past transactions the money an entity is obliged to pay thus sacrificing the future of economic benefits. Liabilities can be in various forms :
Student loan
Credit card balances to be paid
Mortgages
loans
Auto loans
There exist significantly three types of liabilities-
- Non- current liabilities– These are long-term financial borrowings which the company has undertaken which is not expected to be paid off within one year.
- Contingent liabilities– It is an obligation which arises due to occurrence of an event which is uncertain and unpredictable. If the contingency is likely to occur then related amount can be estimated with reasonable level of accuracy. It is recorded with respect to three accounting principles mainly:
Full disclosure principle
Materiality principle
Prudence principle
• Owner’s Equity– It refers to ownership of an individual in the business. It is always recorded at the end of financial period. While such value is indicated by individual’s capital account. It even reflects the money taken out of the business in form of Drawings.
Owner’s equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
Other name for Owner’s equity = Shareholder’s equity
Types of Shareholder’s equity include:
o Retained earnings- When some amount of dividend is kept aside for future use or expansion rather than distributing it completely among the shareholders of the company.
o Common stock- The amount of money so given by the investors as capital investment in return of acquiring ownership in a corporation.
o Preferred stock- It brings in partial ownership along with voting rights in a company with fixed amount of cumulative dividend. It is comparatively a safer investment as at the time of liquidation they are kept at the second position of preference at the time of payment.
o Additional paid-in capital– This term is similar to the contributed surplus, how much money investors paid over par value stock sold to them.
o Treasury stock- It represents the money which is paid to the investors from buying back their stock. It carries a negative balance from company’s perspective; it reduces the organization’s total amount of equity.
Wrapping up – Balance Sheet is thus used to determine risk and return, which lists business assets and liabilities and helps in guiding management decisions. Helps in reporting business financial status to lenders, investors, and other stakeholders and helps in sustaining and grow your business. It helps in analyzing productivity, liquidity and solvency of a business.