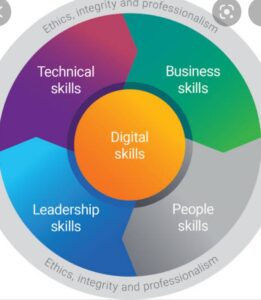
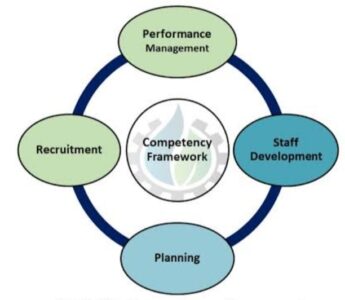
Competency is a term that is much related to an individual’s attributes and inputs. These are defined as behaviours that individuals must acquire to perform the work effectively. It covers the concept of demonstrating performance outputs as well as behavioural inputs.
The core competencies of an organization are its capabilities, knowledge, skills, and resources. Core competencies of an organization are also known by the name of core capabilities, briefing in what way it could perform better than any other company. These competencies lay down a strong base from which business will deliver value to the customer and its stakeholders thus availing new opportunities and growth prospects. It enables a company to stand out from its peers and helps maintain a sustained competitive edge over other competitors within an industry. A company may possess one or more than one wide core competency including:
- Product Quality
- Buying power
- Customer-centric omnichannel support
- Capabilities in terms of design and innovation
- Sales and marketing ecosystem
- Workflows and processes being under automation
- In terms of size
Each competency is defined as a positive feature that contributes to the company’s unique positioning. The development of core competencies would make it difficult for other firms to duplicate the offerings and replicate its success. Identification of core competencies is regarded as a critical step in strategic planning.
A competency framework reflects the knowledge, skills, and attributes required for people within an organization. Every individual role would have its own set of competencies required to perform the job effectively. For the development of this framework, one needs to acquire an in-depth understanding of roles within the business. Approaches that can be adopted include:
- Making use of a pre-set list of common and standard competencies, then further customizing it to the specific needs of the organization.
- Taking help from outside consultants in the development of the framework.
- Building of general organizational framework and making use of it as the basis for other frameworks as well if required.
The creation and building of a competency framework can take a considerable number of effort. Three principles are critical enough when designing a competency framework:
- Involvement of people doing work- this particular framework should not be only developed by HR people alone nor it should be left to the managers who fail to understand exactly what each member of the staff does every day. To fully understand the role, one must go to the source, the person performing the job along with getting a variety of inputs regarding what makes a person successful in the job.
- Communication- many people tend to get nervous regarding performance issues, so at the time of development let them know how it will create and how it will be used. The more it is communicated in advance, the easier it would be its implement.
- Having relevant competencies- an organization or an individual must ensure that all the competencies included must apply to all the roles covered by the framework. If there exist irrelevant competencies, would enable people to experience a hard time relating to the framework. A framework inculcating management roles would certainly involve financial management competency.
Development of Competency Framework
There are four primary steps in the competency framework development process, encouraging people to accept and make use of the final product.
Step-1 Prepare
- Defining the objective- Before one begins to analyze a job, and figure out what each role requires for success, one must ensure to look towards the intent for creating the framework. The planning to use it will impact whom one involves in preparing it and how the scope is determined. For example- a framework for the evaluation of compensation had to cover a wide variety of roles.
- Building a competency framework team- inculcates people from all areas of the business that will utilize the framework to represent the diversity of the organization. It also becomes essential to ponder over the long-term requirements that would help in keeping the framework relevant and updated.
Step-2 Gathering of information- It is considered the main part of the framework. The better information an organization collects, the more accurate a framework would be. It is good to consider which technique would one use to gather information about the roles, and the type of work involved in each one of them. The following techniques are:
- Observation- there is a need to watch people performing their roles and stays suitable in those jobs that involve hands-on labour that can be observed physically.
- Taking interviews of people- Interacting with every person on an individual basis, by choosing a set of people to be interviewed. There would also be a need to interview the supervisor while assessing the job. This helps in gaining insight into people’s views about success.
- Creation of the questionnaire- a survey is an efficient method to collect data. Ensure that much of the time is spent asking the right questions which take into consideration the issues of reliability and validity. While organizations can buy standardized job analysis questionnaires rather than the creation of one’s own.
- Evaluating the work- while analyzing following things need to be considered:
- Business plans, strategies, and objectives
- Principles of the organization
- Job descriptions
- Regulatory or other compliance issues
- Predictions for the future of the organization or industry.
- Customer and supplier requirements
Job analysis consists of a variety of techniques along with considerations that would lead to the generation of more accurate and comprehensive outcomes. In the creation of the framework, one must use a sample of roles across the company to capture the widest range of competencies, relevant to the whole business.
Step-3 Building of the framework- it consists of a grouping of behaviours and skill sets in form of competencies.
- Grouping of statements- Ask the team members to read through the behavioural statements and compile them into piles. The aim is to make three to four piles at the first instance be it manual skills, decision-making, or interpersonal skills.
- Constructing subgroups- breaking down larger piles into subcategories of related behaviour. Generally, there will be three to four subparts of a larger category thus providing a basic structure for the competency framework.
- Refinement of subgroups- further subdividing the larger categories into smaller ones helps in asking why and how the behaviour relates to one another thus revising the grouping as needed.
- Recognition and naming the competencies- Asking the team and the organization to identify the specific competency representing each smaller subgroup of the behaviour. Few of the instances of groupings and subgroupings for general management competencies:
- Recruitment and staffing-
- prepare as per the job description and role specification
- Participation in a selection interview
- Identification of individual training needs
- Implementation of disciplinary and grievance procedure
- Make sure that all legal obligation is met
- Development of staff contracts
- Building salary scales and compensation packages
- Development of personnel management strategy
- To ensure that staff resources go and meet set organizational requirements.
- Training and development
- Delivering training to junior and senior staff
- Recognition of training needs
- Providing proper support to personal development
- Development of training materials and methodologies
Step-4 implementation
After finalizing the competency framework, one needs to keep in mind the principle of communication. It is essential to explain why the framework was developed and how it would like to be used. Certain tips for implementation of the framework include;
- Linking to the business objectives- there is a need to make connections between individual competencies and organizational goals and values as much as possible
- Rewarding the competencies- scrutinizing the policies and practices
- Providing coaching and training
- Developing framework on the earliest basis. One wants the document to be used and not filed away.
- Communication- the more honest and open a person is throughout the conversation the better the results and the better the chances of the project achieving objectives.
Conclusion
Building a competency framework is recognized as an effective method to assess, maintain and monitor the knowledge, skills, and attributes of people within the organization. The framework so drafted helps in measuring current competency levels to ensure that the staff members have much expertise needed to add value to the current business operation. Enables managers to make informed decisions about talent recruitment, retention, and succession strategies.